KMM 🦁

Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile (KMM) is a cross-platform mobile development technology that lets developers write code once and use it on Android and iOS platforms.
KMM is built on top of the Kotlin language — a modern and expressive programming language gaining popularity among developers due to its simplicity and flexibility.
Development Environment
-
With the KMM shared module and Android application, as both are written in Kotlin, it is recommended to use Android Studio (with the KMM plugin).
-
With the iOS application, Xcode will be the best option for iOS developers to develop user interfaces. To debug the shared Kotlin code while running an iOS app through Xcode, consider using the Kotlin Native Xcode Plugin.
Architecture
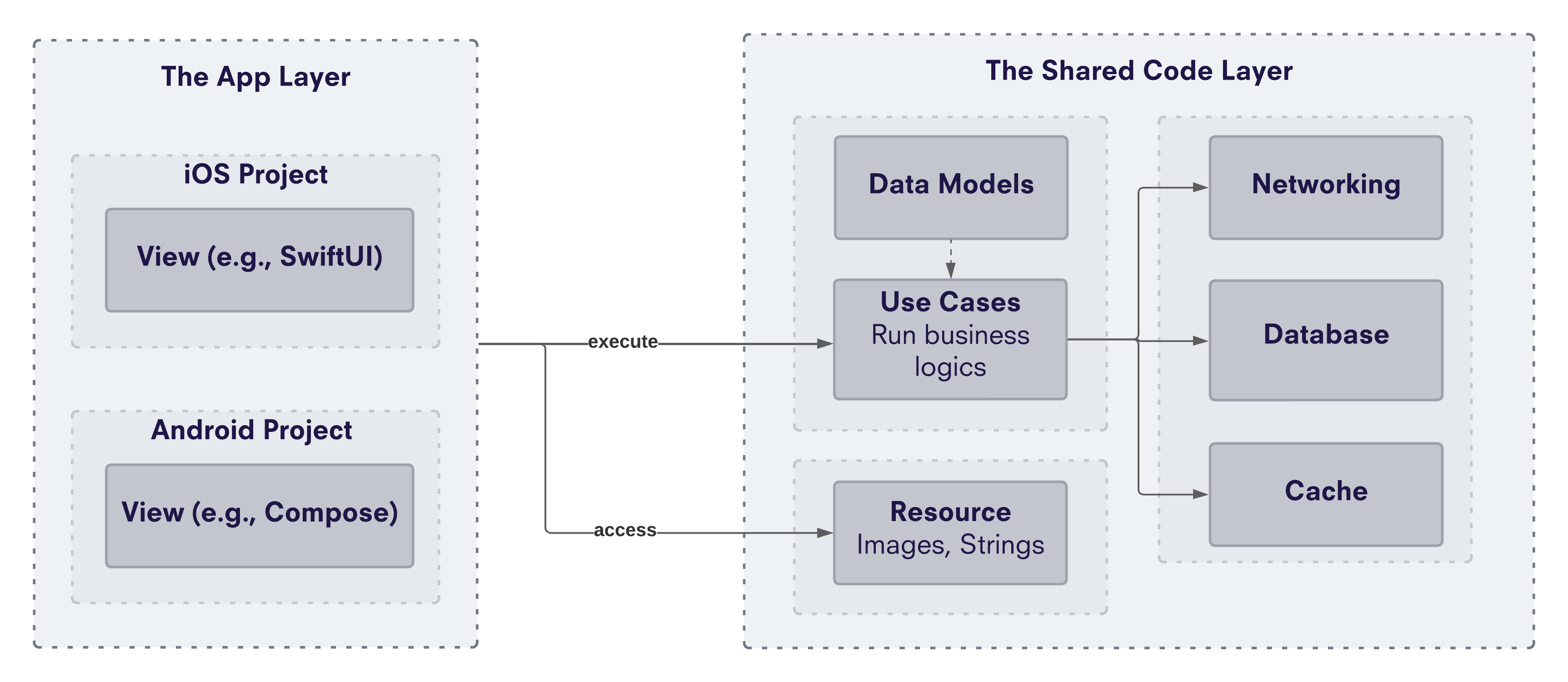
The architecture of a KMM project consists of two layers:
- The App Layer (App module) contains the native code in Kotlin for Android and Swift for iOS. This layer includes the application’s UI framework (e.g., SwiftUI for iOS and Jetpack Compose for Android), navigation, and other platform-specific functionalities. The app layer uses the shared code layer to build the app for each platform.
- The Shared Code Layer (KMM module) contains the shared code written in Kotlin and used across Android and iOS platforms. This code can include business logic, data models, network interactions, local database (offline data), and resources. The shared code layer is compiled into a library both platforms can use.
The KMM project’s architecture can be illustrated with the following diagram:
Project Structure
The following structure and directories should be followed for the KMM shared module (shared):
└── a-kmm-project
├── build.gradle.kts
├── androidApp
├── iosApp
└── shared
├── build.gradle.kts
├── shared.podspec
└── src
├── androidMain
├── androidTest
├── commonMain
│ ├── kotlin
│ │ ├── package-name (e.g., co.nimblehq.kmm.shared)
│ │ │ ├── data
│ │ │ │ ├── local
│ │ │ │ ├── remote
│ │ │ │ └── repository
│ │ │ ├── di
│ │ │ ├── domain
│ │ │ │ ├── model
│ │ │ │ ├── repository
│ │ │ │ └── usecase
│ │ │ └── helper
│ └── resources
├── commonTest
├── iosMain
└── iosTest
-
androidApp: contains the native Android application. This folder should follow theappfolder in the Android Structure. -
iosApp: contains the native iOS application. This folder should follow the iOS Structure. -
shared(KMM module): contains the shared code written in Kotlin and used across both platforms.
Project Configurations
-
Use Kotlin DSL to define and configure the project configurations for the
sharedandandroidAppmodules. -
To embed and provide project credentials and configurations for the
sharedmodule, use BuildKonfig.
Dependency Injection (DI)
The KMM project uses Koin as the main DI framework in the shared and androidApp modules, while the iosApp module injects Koin components from the shared module and might use its preferred DI method for the rest.
Networking
Ktor is the recommended networking framework for the KMM project. It adds the capability to make requests, handle responses, and includes a variety of plugins, such as authentication, serialization.
Resources
These are two ways to manage the KMM project’s resources:
Independent resource files
Add resources separately in both androidApp and iosApp modules and then maintain them independently.
Shared resource files
Add all resources to the shared module and use the same files in both platform modules. This approach saves the maintenance effort with only resource files in the shared module.
- Consider using Moko-resources (recommended by Phrase) to optimize sharing project resources in the KMM project.
Testing
The KMM project follows the general guidelines of testing. Since the shared module of a KMM project is written in Kotlin, it shares many of the principles, conventions, and best practices of Android development. For the conventions regarding test directory structure, test class, mock object, and test case naming, refer to the Android testing methodology.
Strategy
The shared module contains the non-UI components, such as use cases, repositories, and data, as well as domain models and their mappers. The unit tests must cover all the use cases, repositories, and other relevant classes, such as remote and local data sources, response mappers, etc., following the strategies outlined here (see Repository, UseCase, and Service/Manager).
Libraries
The following libraries are preferred when writing tests and generating code coverage report for the shared module:
- Mockative for mocking/stubbing
- Kotest for assertions
-
Turbine for testing
kotlinx.coroutinesFlow - Kover for generating code coverage report
The androidApp and iosApp modules can use their libraries of choice agreed upon by the respective chapters.
Naming
-
The
sharedmodule does NOT support commas in the method names within backticks, even though the tests run without issues. To eliminate the IDE warning, replace the commas with hyphens.fun `When age is less than 18, it emits isAdult as false`() { // arrange // act // assert }fun `When age is less than 18 - it emits isAdult as false`() { // arrange // act // assert }