User Experience

User Experience is a person’s perceptions and responses resulting from the use and/or anticipated use of a product, system or service.
Why Does The Team Use UX Design?
The benefits of User Experience (UX for short) design are two-fold:
- Great UX is what makes for a great experience when using a product
- The better the User Experience, the better the adoption rate of the product
The team uses UX design because that’s what generates happy customers, and inherently increases sales. Those two goals are the main indicators of a good UX.
User Experience design is the process of enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product.
UX Design Process
The first consideration should be how to align the user’s goals with the business goals.
As a general rule, the business goals must revolve around providing a useful, usable, and delightful experience.
- Useful: The user has a problem. Solve that very problem.
- Usable: The product must be usable in that it has to be instinctive with no learning curve.
- Delightful: It’s not a bad thing if the user enjoys using the product ;)
A happy, well-informed user, will return. A frustrated one won’t. Providing a good experience triggers a virtuous circle:
- If the user finds what (s)he is looking for easily, the user’s goal is achieved. This created a good experience.
- A user with a good experience is more likely to buy and/or return to the product, increasing the conversion rate.
- A user who buys and/or returns to the product is most likely to recommend it to friends and family, increasing traffic and revenues.
Define The “Why”s
Why are we designing this product? Why will people use it?
The “why”s have to be documented in such a way that, to anyone who asks, the team can explain exactly the reasons for designing the product, and for designing it specifically in the way they did.
The “Why” should be the driving force of the product. It is what gives it a meaning, a story, a theme.
User Research
User research serves as the starting point for a project, as it provides insights into the users, their behavior, goals, motivations, and needs.
Additionally, it reveals how they currently navigate the system, where they encounter problems, and, most importantly, how they feel when interacting with the product.
Creating Personas
A persona is not the customers the team wants. It’s the customers they have, or the customer who’s out there waiting to be picked-up.

Personas are fictional, but they represent a selection of the real-life audience and its behaviors. The team builds user personas for qualitative and, to some degree, quantitative user research.
Creating the Journey (User Flow)
Designing a satisfying UX involves meticulously planning a User Journey. It is about helping users find what they are looking for through an intuitive process.
Customers will, in any case, follow a certain process/journey when performing an action. Their process is often based on previous experiences they had with other products.
Creating the User Journey is about controlling their process to ensure that it is not going to impact their experience negatively.
This is achieved by creating User Flows.
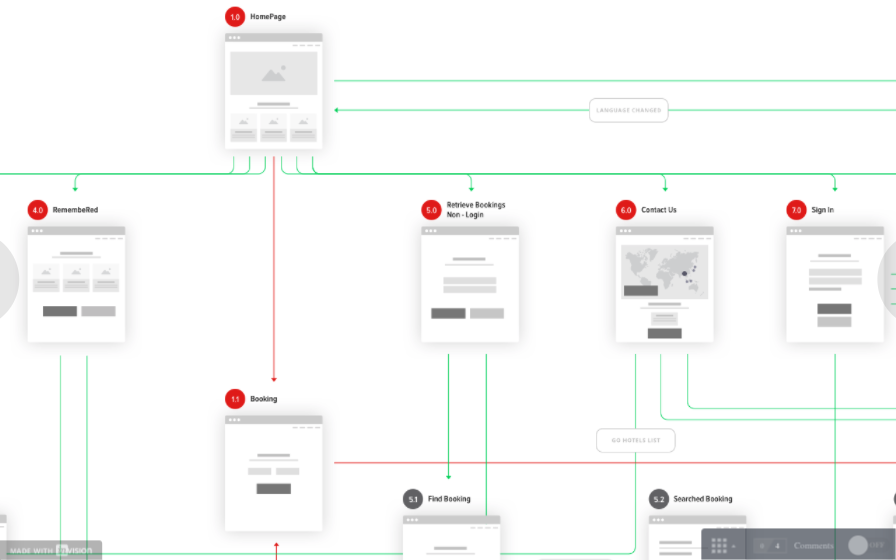
Wireframing
For starters:
- Wireframes MUST NOT CONTAIN ANY COLOR so as not to distract the client from the main focus: the User Experience.
- Wireframes MUST BE DESIGNED WITH SKETCH AND PUBLISHED ONLINE. No paper sketches. This is to safeguard the work done. It is also much easier to share and edit.
- Wireframes MUST LOOK PIXEL PERFECT. Even though they are just wireframes, they should look elegant and accurate. Almost alike the UI. It helps the client understand the various interactions.
Wireframing, in UX design, refers to an illustration or diagram of a website, software, or app page that looks at the allocation of space on that page, the distribution of images and content.
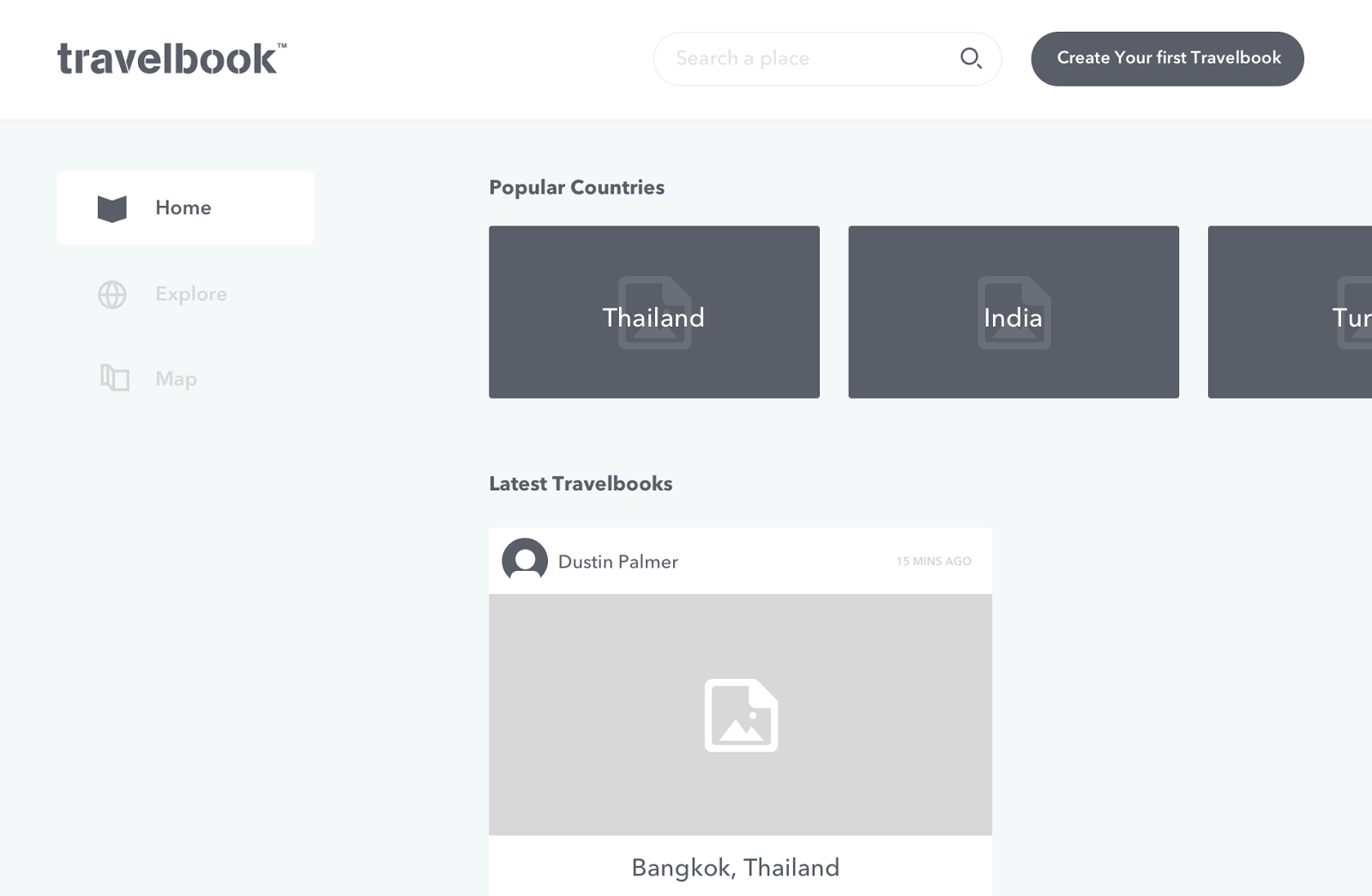
Wireframes should answer those questions:
- How content is prioritized?
- What functions are available?
- What behavior is intended and accommodated?